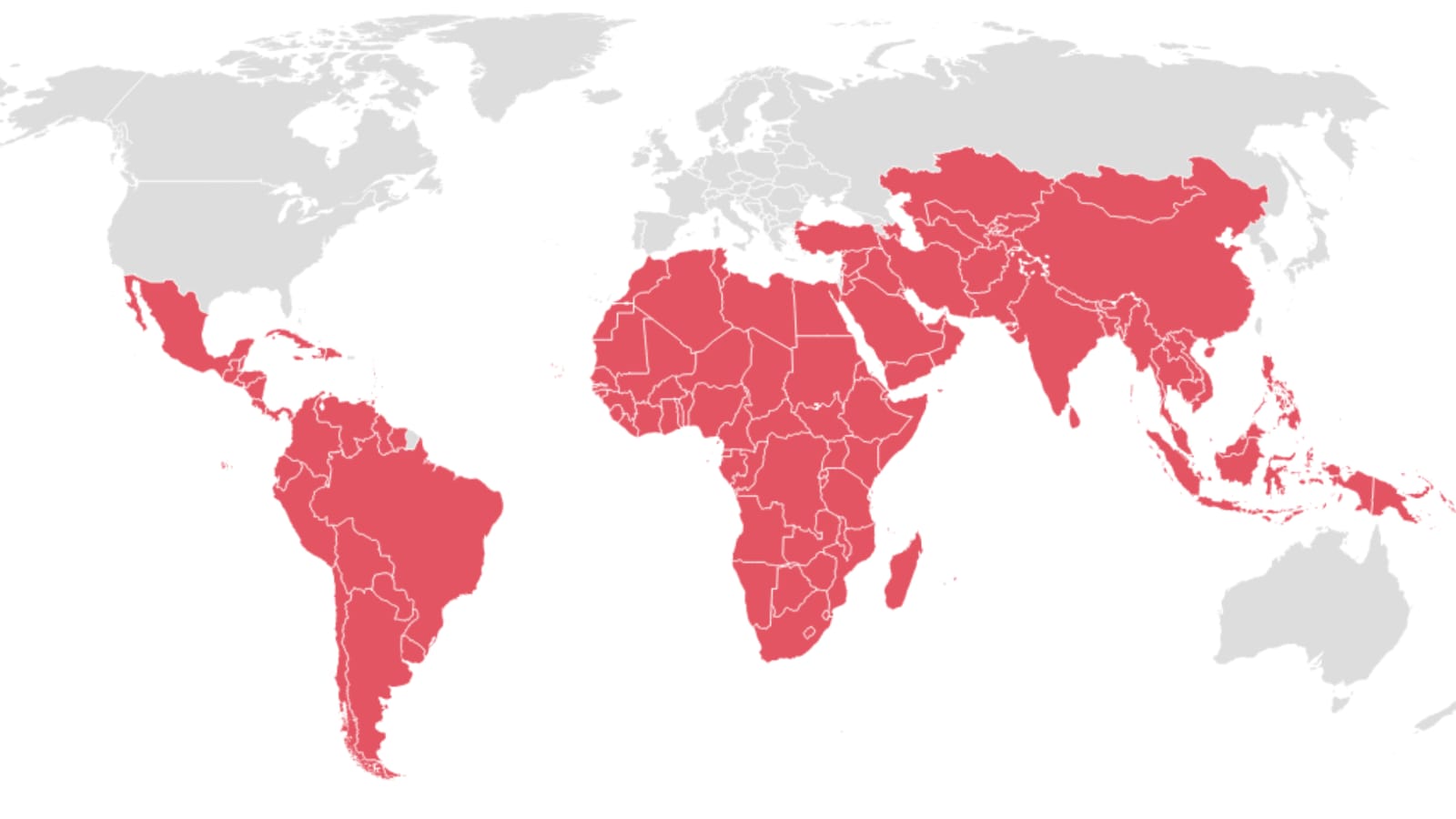
What’s the fuss about the Global South?
The rebalancing of economic power towards the Global South challenges the traditional dominance of the Global North and has prompted a re-evaluation of global governance structures
The Global South is a term that has gained prominence in recent years, stirring up debates and discussions across various disciplines such as international relations, economics, and development studies. It refers to a group of developing countries primarily situated in the southern hemisphere, spanning across Africa, Latin America, and Asia. This article aims to delve into the reasons behind the growing attention towards the Global South, the implications of this focus, and the opportunities and challenges it presents for these regions.
Historical Context
To fully understand the significance of the Global South, it is essential to trace its origins back to the historical context that shaped its emergence. The concept can be seen as a response to the divide between the rich, industrialized countries of the Global North and the relatively poorer, developing countries of the Global South. This divide is rooted in a history of colonization, exploitation, and unequal power dynamics between the Global North and South.
Colonization imposed by European powers during the 15th to 20th centuries left lasting legacies that have influenced the economic, political, and social disparities still prevalent today. The exploitation of resources, forced labor, and the creation of dependent economies by the colonizers resulted in deep inequalities that continue to persist. The concept of the Global South challenges this historical imbalance by highlighting the autonomy, diversity, and resilience of these regions and their collective response to neocolonialism.
Geopolitical and Economic Rebalancing
The attention towards the Global South has gained momentum in recent decades as there has been a significant shift in global economic power and geopolitical dynamics. This shift has been characterized by the rise of emerging economies such as China, India, Brazil, and South Africa, which have been experiencing unprecedented economic growth. These countries have become major players in the global arena and have reshaped the global economic architecture.
The rebalancing of economic power towards the Global South challenges the traditional dominance of the Global North and has prompted a re-evaluation of global governance structures. Institutions such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) have faced criticism for their Western-centric approaches and the marginalization of the Global South in decision-making processes. Consequently, there has been a push for greater representation and voice from these regions in global governance institutions to ensure a fairer and more equitable international order.
Development and Global Challenges
The Global South is home to a majority of the world’s population and faces numerous development challenges, including poverty, inequality, and inadequate access to basic services such as healthcare and education. However, these countries also possess immense potential for growth and development. They have rich reserves of natural resources, a young and dynamic workforce, and growing consumer markets.
In recent years, the Global South has made significant strides in various sectors such as technological innovation, renewable energy, and social entrepreneurship. These regions have also been at the forefront of addressing global challenges such as climate change, migration, and peacebuilding. The Global South has been instrumental in advocating for environmental sustainability and pushing for climate justice, given that these regions are disproportionately affected by the adverse impacts of climate change.
South-South Cooperation and Regional Integration
An important aspect of the Global South discourse is the emphasis on South-South cooperation and regional integration. Countries within the Global South are increasingly collaborating and exchanging knowledge, experiences, and resources to address shared challenges and capitalize on mutual opportunities. This cooperation takes various forms, including trade agreements, development assistance, and knowledge sharing platforms.
Regional integration initiatives, such as the African Union (AU), the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), and the Mercado Común del Sur (MERCOSUR) in Latin America, have gained traction and are seen as vehicles for collective action. These regional blocs foster economic integration, political cooperation, and social development within their respective regions, effectively empowering the countries of the Global South to negotiate as a collective force in the international arena.
Challenges and Roadblocks
While the Global South presents immense potential and opportunities, it also faces numerous challenges that need to be addressed. Some of these challenges include political instability, corruption, inadequate infrastructure, and institutional weaknesses. Additionally, the Global South also often grapples with social issues such as gender inequality, youth unemployment, and limited access to quality healthcare and education.
Furthermore, the Global South’s reliance on natural resources can result in environmental degradation and economic vulnerability, especially in the face of global economic fluctuations. There is a need for sustainable development practices that prioritize environmental conservation, social inclusion, and economic diversification.
Conclusion
The focus on the Global South signifies a shift in the traditional power dynamics and global economic order. It brings attention to the diversity, resilience, and potential of the developing countries situated primarily in the southern hemisphere. The recognition of the Global South as an influential force challenges the historical legacies of colonization and neocolonialism, calling for greater representation and inclusivity in global governance structures.
By addressing the unique development challenges and opportunities of these regions, there is a potential for the Global South to drive sustainable and inclusive development on a global scale. The Global South’s emphasis on South-South cooperation, regional integration, and collective action is instrumental in reshaping global processes and addressing common challenges. However, it is crucial to address the challenges that hinder progress, including political instability, corruption, and environmental degradation.
Ultimately, the growing focus on the Global South is an opportunity for the world to recognize and amplify the voices, contributions, and aspirations of these regions. It is a call for a more equitable global order that values collaboration, social justice, and sustainable development for the benefit of all humankind.
Dr Brian Reuben, international business development expert is the Executive Chairman of the Brian Reuben Policy Group and the Chief Executive Officer of the Africa Economic Summit Group.



